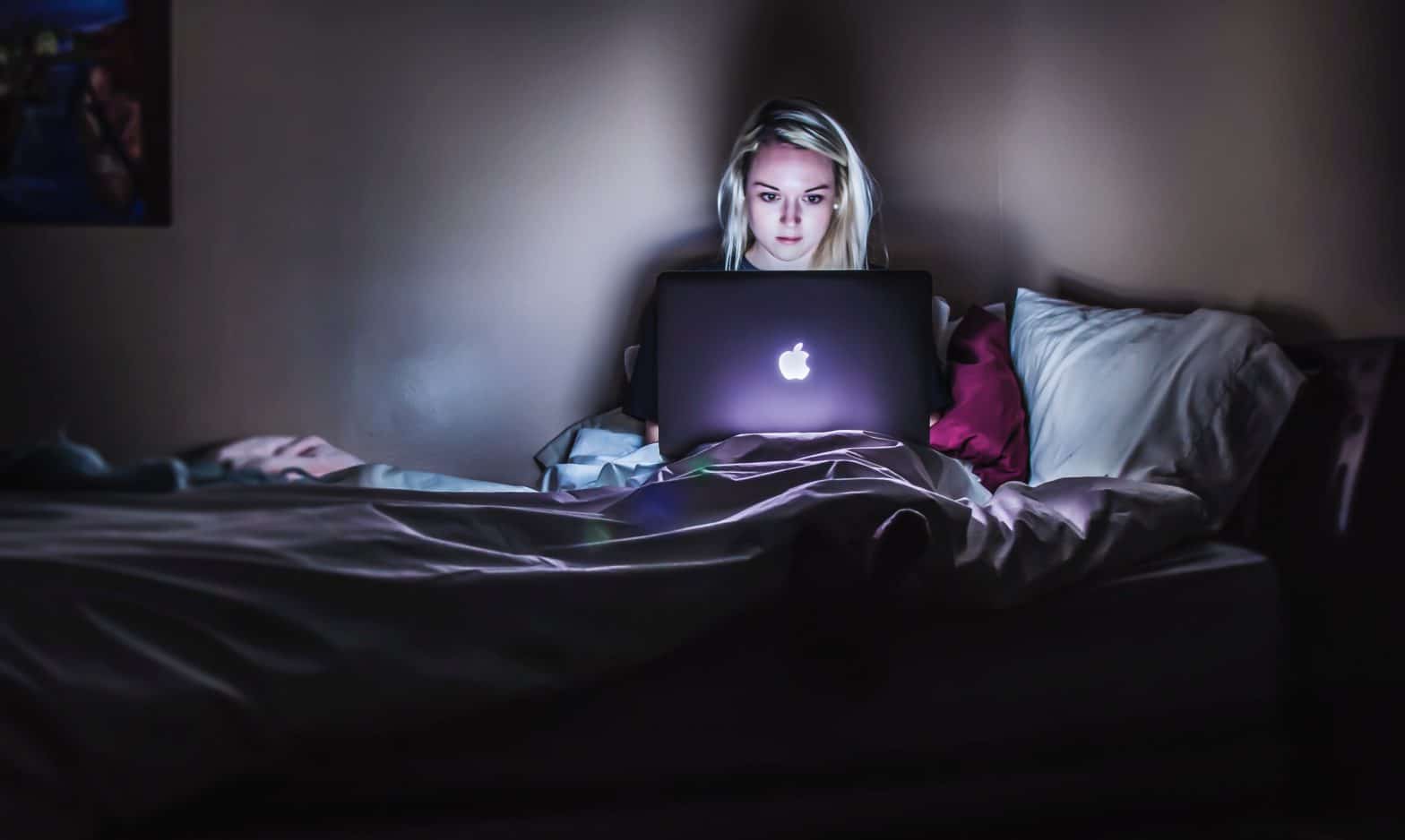
Blue light reduces quality of sleep. Exposure to blue light after dark keeps you up late at night. Exposure to sunlight during the day is critical. The blue light is very bright and tends to illuminate the inner surface of your nose and throat. If you’re under the influence of blue light, you’ll feel more awake by your next shift. When you wake up in the darkened room from your night shift, you’ll feel pretty refreshed to the point of disorientedness. How does it work? Your blood contains blue light, which helps with sleepiness. Bright blue light will actually cause your body to produce more serotonin to sleep harder.
What the blue light causes are the hormone melatonin. Melatonin releases more melatonin, because sleepiness increases its impact. To create a strong connection between melatonin and blue light, it takes at least one (or more) of three things, depending on the body. The first one is the amount of blue light (that is blue light), and the second one is that melatonin can influence your body to release more melatonin.
The third one is the amount of blue light (that is yellow light and blue light, rather than blue-in color, which tends to create the “red glow” blue glow). When you first feel free of blue light, you should put that blue light away until you wake up on the third night of the night.